Your credit score
it is one of the most critical factors in your financial life. Your credit
score determines if you are approved for a loan or line of credit. Credit
scores are used to determine: if you will be hired for a job, interest rates,
terms and conditions, downpayment costs, rates for medical and other insurance
coverage, approval for cable and internet service and more.
A credit score is
a mathematically calculated number developed by the Fair Isaac Corporation
(FICO) that lenders use to rate potential customers in determining the
likelihood that a customer will pay their bills on time.
A credit score or
credit rating is determined by using five main criteria as defined by
MyFico.com: your payment history which accounts for 35% of your credit score,
the amounts owed which accounts for 30% of your credit score, the length of
your credit history which accounts for 15% of your credit score, new credit
which accounts for 10% of your credit score, and the types of credit used which
accounts for 10% of your credit score.
Payment history
shows the history of how you paid your bills either on time or late. Amounts
owed shows the total amount of credit you have available. The length of history
indicates how long you have had credit. New credit indicates how many times you
have applied for new credit. If you open too many new accounts in a short
period of time this may lower your credit score. The types of credit used
indicate the types of accounts you have such as revolving or installment
accounts. Revolving accounts are usually credit cards and installment accounts
are usually mortgages, auto loans, etc.
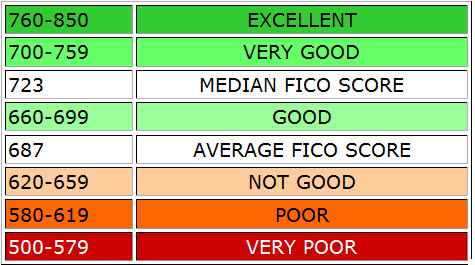
The FICO credit
score model ranges from 300-850 with 850 being an excellent score and 300 being
the worst score. The higher the credit score the lower the interest rate you
will receive for a loan or line of credit. Possessing a good credit score can
save you thousands of dollars in interest over the life of the loan or on a line
of credit. A good credit score is generally in the range of 720 or above but may
vary from lender to lender.
When applying for
credit or a loan if all three credit scores are pulled, the middle score is
generally the score used with the application.
Your credit score varies from each bureau because each agency collects
their own data from various sources and may collect different data for the same
account. Your score can vary anywhere from 5-40 points between the three credit
bureaus.
Your credit score changes due to updates to your credit file which changes based on account activity such as balance changes or additions to your credit file (i.e. new accounts or deletion of older negative accounts more than 7 or 10 years old). As a result, you may see a difference in your score from one month to the next. Here are some guidelines to help you determine how payments affect your credit score:
Payments
- Paying a 30 day late payment can increase a score by 3-80
- Paying collection accounts can increase a score by 20-90 points
- Paying public records (judgments, tax liens, Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy) can increase a credit score by 75-150 points
- Paying a charge-off can increase a credit score by 50-100 points
- Paying a repossession can increase a credit score by 50-100 points
- Paying delinquent student loans which can increase a credit score by 50-80 points
The major disadvantage of credit scoring is that it relies on information
in your credit report that may contain errors. It is estimated that 75% of
credit reports contain at least one error.
That is why it is so important that you check your credit report at
least once a year to ensure that all information is accurate and up to date.
If you plan on
purchasing a large item such as a car, house or investment property, it is best
to pull your credit yourself to see if any negative items appear so you can fix
those issues before applying for a loan. The best way to understand your credit
score is to do research and read the information that is included when you
order your credit report.
No comments:
Post a Comment